Table of contents
Introduction

Welcome to the {{titleApp}}. {{acronym}} was created to
provide information about the variability of the {{phenotype}} population to the
scientific/medical community.
It is useful for filtering polymorphisms and local variations in the process of
prioritizing candidate disease genes. {{acronym}} currently stores information on
109 unrelated {{phenotype}} individuals.
{{acronym}} structure
{{acronym}} has the following architecture:
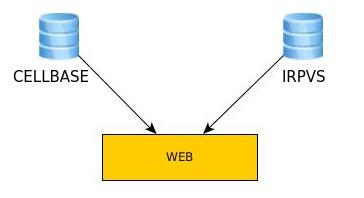
It consists of a proprietary database where variants and their associated
counts are stored. VCF files are introduced into the database and a web page is used to visualize such
variants. A graphical interface is provided for displaying variants with additional enriched information related to annotated from Cellbase database.
Main page
To start using {{acronym}}, click on the following link:
https://irpvs.clinbioinfosspa.es/.

On the main page you can see a start button (1), a login (2), a "?" (3) for {{acronym}} information.
Read and accept "Terms and conditions for the use of the {{acronym}} database"
 .
.
When the user clicks on "Start" button  , the Search tab appears.
, the Search tab appears.
 , the Search tab appears.
, the Search tab appears.
Search
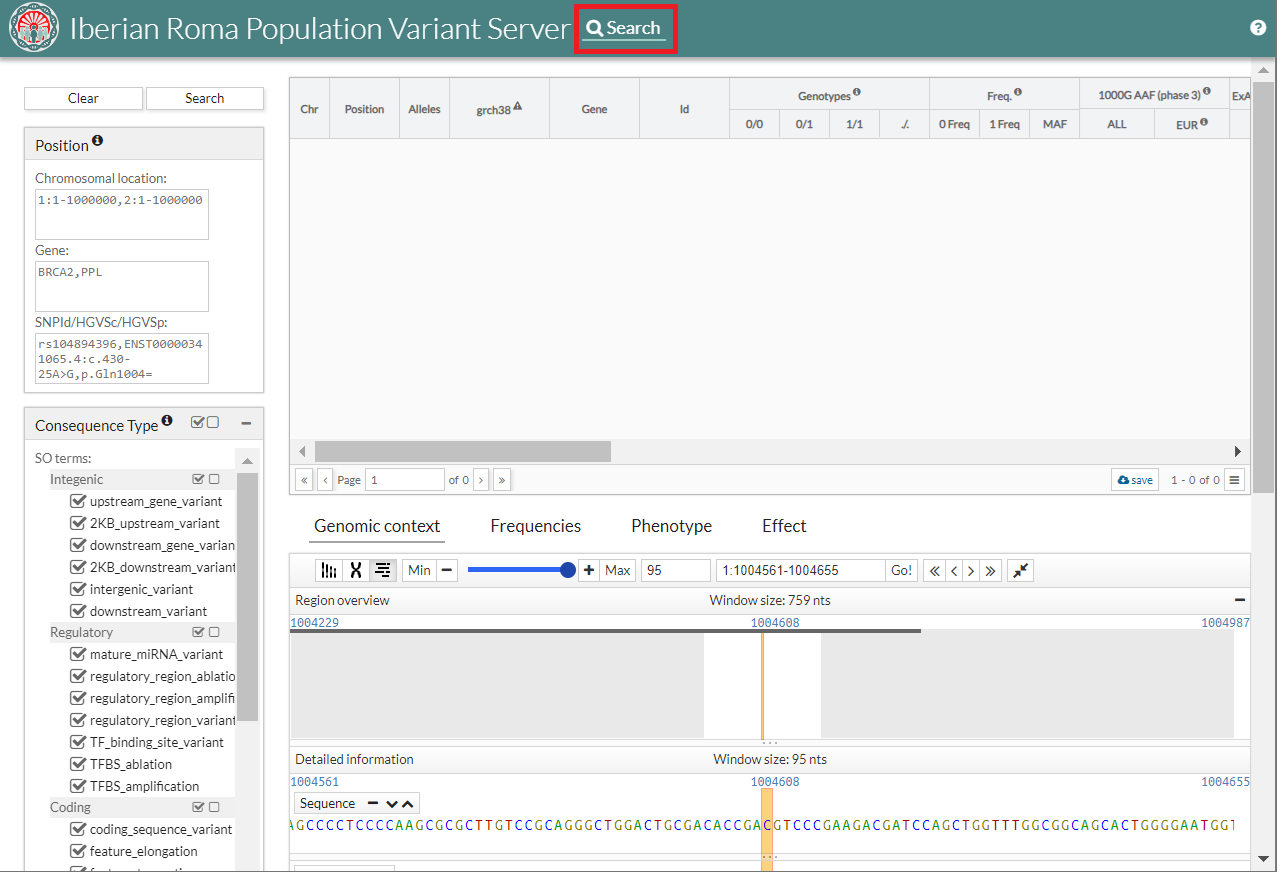
Variant filtering by position or sequence ontology term
1. Position:
This filter has three possibilities:
This filter has three possibilities:
- Chromosomal Location in hg19 coordinates: Region where narrow your search. Chromosome: Start-End. The maximum size is 2,310,000 bases.
Example: 1:876400-879676. - Gene: Get variants for a particular gene (or a set of genes separated by commas. The maximum number of genes allowed is 5.
Example: BRCA2,PPL. - SNP ID/HGVSc/HGVSp: You can search variants by SNP ID, HGVS transcript nomenclature (HGVSc) or HGVS
protein nomenclature (HGVSp). In the last case, gene is mandatory. The maximum number of SNP ID, HGVSc and HGVSp is 10.
Example 1. SNP ID: if the snp doesn't exist in the database, it displays the message: "No results for this SNP ID"
Example 2. HGVSc:
Example 3. HGVSp:
2. Consequence Type:
You can filter variants by selecting Sequence Ontology terms.
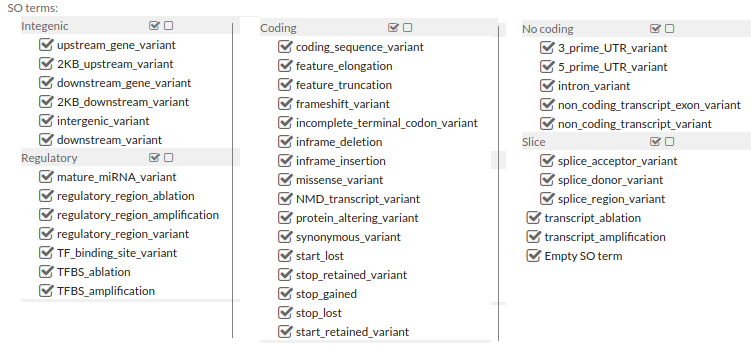
You can filter variants by selecting Sequence Ontology terms.

Highlight variants
You can highlight variants(i.e. no filter is applied) using thresholds for SIFT, Polyphen, CADD or
GERP values.
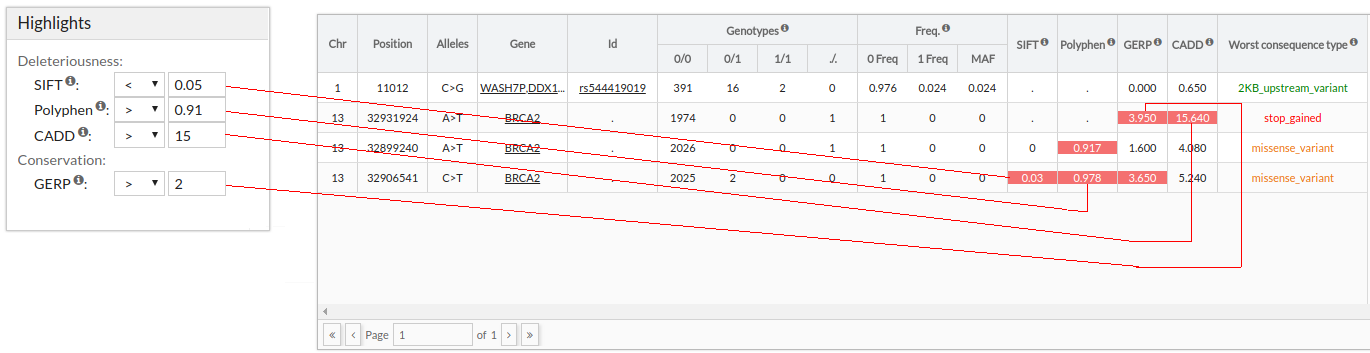
IMPORTANT: When there are several Consequence types for a given variant, the worst one is selected according to cellbase. To see all of them, select the variants and click on the Effect tab below.
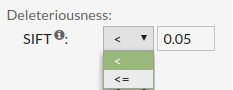
- SIFT score predicts whether an amino acid substitution affects protein function. SIFT
value less than 0.05 represents a 'deleterious' prediction whereas SIFT value greater than or
equal to 0.05 represents a 'tolerated' prediction.
Allowed values are between '0' and '1'.
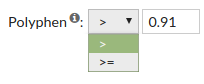
- Polyphen score predicts the possible impact of an aninoacid subsitution on the structure
and function of a protein. Polyphen scores can be benign (<0.446), possibly damaging
(0.446-0.908) or probably damaging (>0.908).
Allowed values are between '0' and '1'.
- CADD tool scores the deleteriousness of snvs and indels. Higher values indicate more
likely to have deleterious effects.

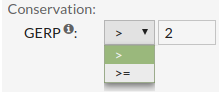
- GERP score estimates the level of conservation of positions. Positive scores represents
a
substitution deficit and this indicate that a site may be under evolutionary constraint.
Negative scores indicate that a site is probably evolving neutrally. Some author suggest
that scores >=2 indicate evolutionary constraint and >=3 indicate purifying
selection.
Allowed values are between '-15' and '7'.

IMPORTANT: When there are several Consequence types for a given variant, the worst one is selected according to cellbase. To see all of them, select the variants and click on the Effect tab below.
Results
Once filters/highlights are selected, by clicking on the search button, the query is sent to the database. Results will be displayed in a data table with the variants of the {{acronym}}
database enriched with additional annotation information provided by
Cellbase.
Cellbase is a database that integrates the most relevant biological information about genomic features and proteins, gene expression regulation, functional annotation, genomic variation and systems biology. Cellbase use the most relevant repositories such as Ensembl, Uniprot, Clinvar, COSMIC or IntAct among many others. For more information about cellbase click here.
Cellbase is a database that integrates the most relevant biological information about genomic features and proteins, gene expression regulation, functional annotation, genomic variation and systems biology. Cellbase use the most relevant repositories such as Ensembl, Uniprot, Clinvar, COSMIC or IntAct among many others. For more information about cellbase click here.

Fields

For each variant, the following information is shown:
- Chr: Chromosome position.
- Position: Variant position.
- Alleles: Alleles of the variant.
- Grch38: The coordinates in this column are given for informative purposes only. They result from a liftover from the reference GRCh37 to GRCh38. As such, some inaccuracies can be expected due to differences between the reference sequences.
- Gene: Gene or genes in which the variant is located.
- Id: rs variant identifier.
- Genotype: Genotype counts:
- 0/0: homozygous reference
- 0/1: heterozygous
- 1/1: homozygous alterntive
- ./.: missing
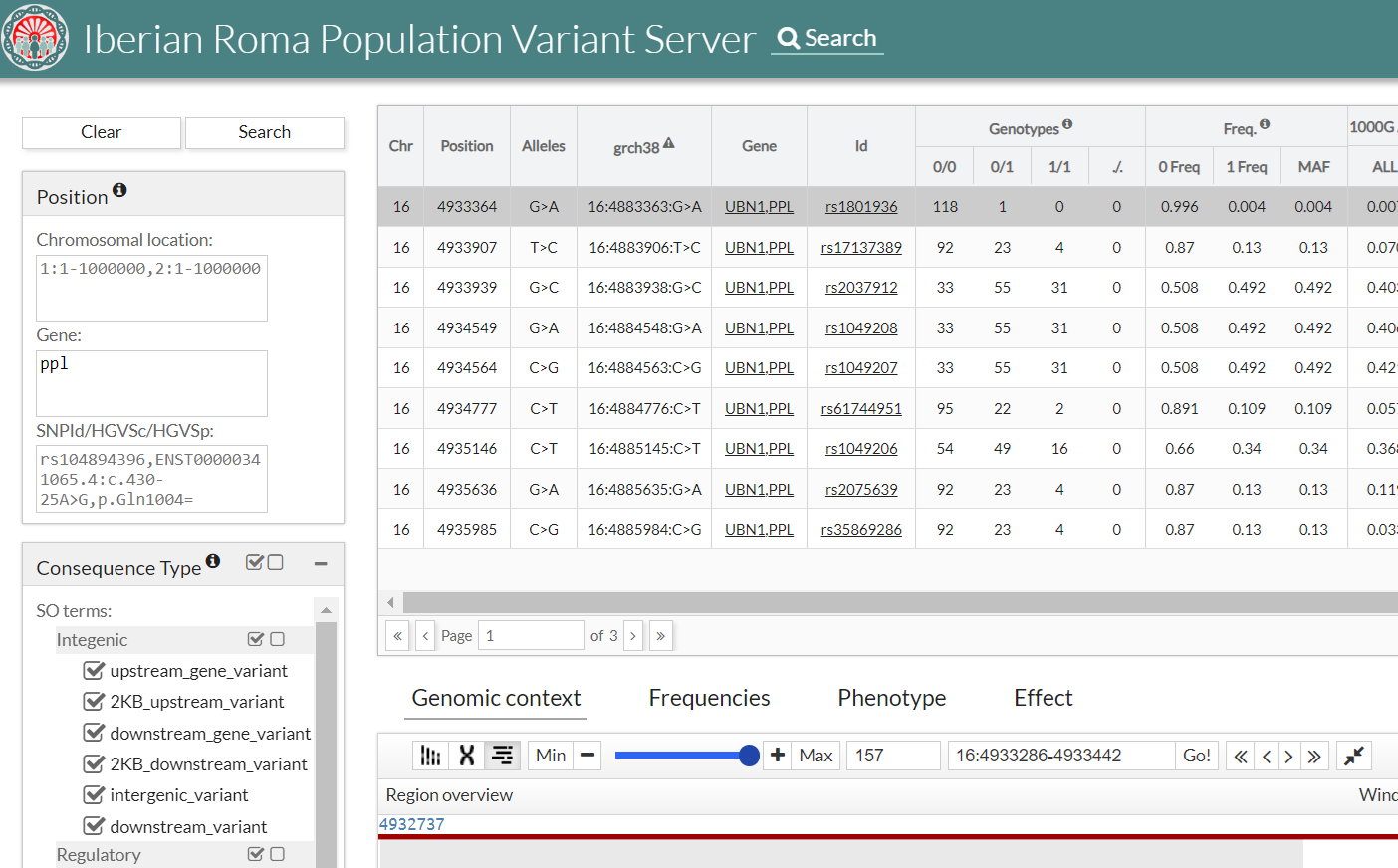
- Freq.: Allele Frequency:
- 0 Freq: allele frequency for reference
- 1 Freq: allele frequency for alternative
- MAF: Minor Allele Frequency, the lowest value between 0 Freq and 1 Freq
- 1000G AAF(phase 3): Alternate Allele Frequency in 1000 genomes project database (phase 3)
- ALL: Frequency recorded in 1000G for the variant selected for the entire population.
- EUR: Frequency recorded in 1000G for the variant selected for the European population.
- ExAC AAF: Alternate Allele Frequency in Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC) database
- ALL: Frequency recorded in ExAC database for the variant for the entire population.
- ESP 6500 AAF: Alternate Allele Frequency in Exome Sequencing Project (ESP)
database
- ALL: Frequency recorded in ESP 6500 database for the variant for the entire population.
- EA: Frecuency recorded in ESP6500 database for the variant for European Amerindian.
- MGP+IBS AAF: Alternate Allele Frequency in Spanish local population in Medical Genome Project (MGP) and Iberian population in Spain (IBS) from 1000 genomes project database
- gnomAD AAF: Alternate Allele Frequency in Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD).
- GENOME ALL: Frequency recorded in gnomAD database for the variant for the entire population (genome).
- EXOME ALL: Frecuency recorded in gnomAD database for the variant for the entire population (exome).
- SIFT: SIFT score predicts whether an amino acid substitution affects protein
function.
SIFT value less than 0.05 represents a 'deleterious' prediction. SIFT value greater than or equal to 0.05 represents a 'tolerated' prediction - Polyphen: Polyphen score predicts the possible impact of an aninoacid subsitution on the structure and function of a protein. Polyphen scores can be benign (<0.446), possibly damaging (0.446-0.908) or probably damaging (>0.908).
- GERP: GERP score estimates the level of conservation of positions. Positive scores
represents a substitution deficit and this indicate that a site may be under
evolutionary constraint.
Negative scores indicate that a site is probably evolving neutrally. Some author suggest that scores >=2 indicate evolutionary constraint and >=3 indicate purifying selection. - CADD: CADD tool scores the deleteriousness of snvs and indels. Higher values indicate more likely to have deleterious effects
- Worst Consequence type: Worst consequence type found among all transcripts by Cellbase. We also collect this information from the Cellbase database that is annotated with ensembl. You can find the information about the calculation of the consequence type of ensembl here.
- Transcript of interest: annotation corresponds to the transcript introduced in 'SNP ID/HGVSc/HGVSp' textbox. If empty, annotation corresponds to the canonical transcripts.
To see more information about transcripts see tab Effect.- Transcript ID
- HGVSc: HGVS coding sequence name
- HGVSp: HGPVS protein sequence name
- Exon: exon number(s) / total
- Consequence type
- Phenotypes: Information about relationships among human variations and Clinvar and
Cosmic databases.
- Clinvar: Clinvar is a public archive of reports of the relationships among human variations and phenotypes hosted by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and funded by intramural National Institutes of Health (NIH) funding. In this column we note the phenotype of the variant that appears in Clinvar.
- Cosmic: Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer (COSMIC), is the world's largest and most comprehensive resource for exploring the impact of somatic mutations in human cancer.In this column we note the phenotype of the variant that appears in Cosmic.
Other features table result
- Resize:
The size of the columns in the table is modificable. If the user wants to make the width of a column smaller or bigger, just place the mouse on the edge of the column header that you want to modify until the icon of the two arrows appears, press the mouse and move towards the right or to the left becomes larger or smaller respectively.
-
Pagination:
The table shows the results in page form, that is, it shows the first ten results, and to see the next ones we must press the bottom button of the table ">" or move with the wheel of our mouse down on the table. To see the previous results, press the lower button "<" or move with the mouse wheel up. If you click on the ">>" button, the results of the last page will be shown, in the same way if you press "<<" the results of the first page will be shown. It is also possible to directly access a page by entering the desired number in the lower input of the table.
-
Show/Hidden columns:
The information in the table can be filtered. If we press the button with the three stripes that is in the lower right part of the table, a drop-down is shown with all the columns of the table. Marking or unchecking the columns will be displayed or not in the table.
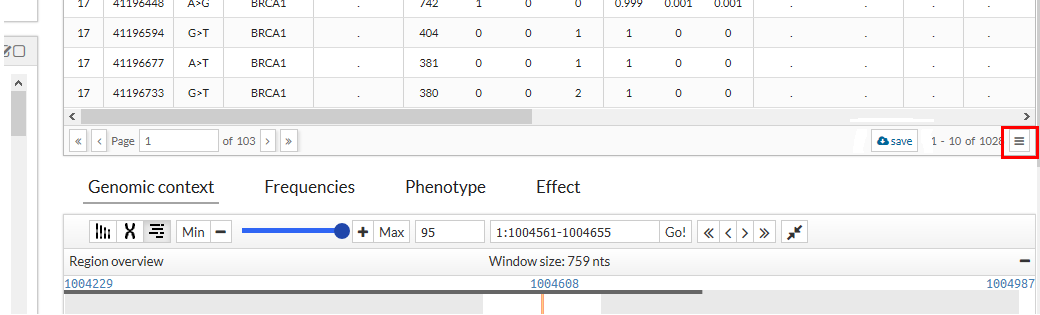
By default exist some fields hidden. For example:- phastCons: phastCons scores represent probabilities of negative selection and range between 0 and 1.
- phyloP: phyloP scores measure the level of conservation of positions. Positive scores measure conservation whereas negative scores measure acceleration.
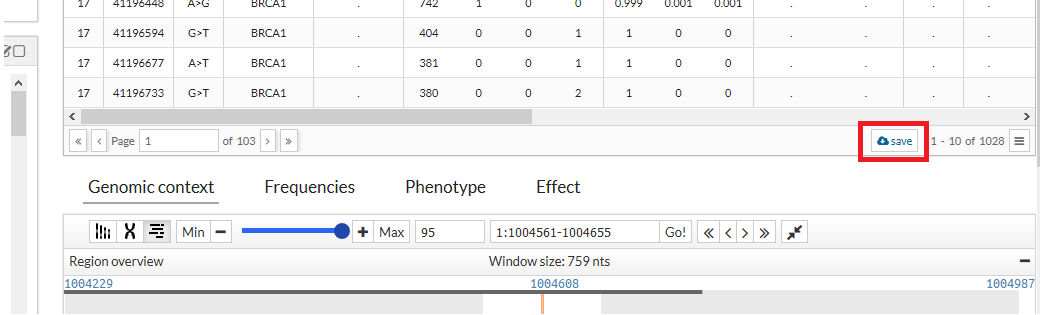
- Save data:
By clicking on the save button at the bottom of the table, variants can be downloaded.
What we will obtain is a tabular file with the name of the variants and the maf of the {{acronym}}, both genotypes and their frequency. Only get the data show in the screen (max 10 registers).
Extra information
If the user clicks on a given variant in the table, some extra information is shown below.
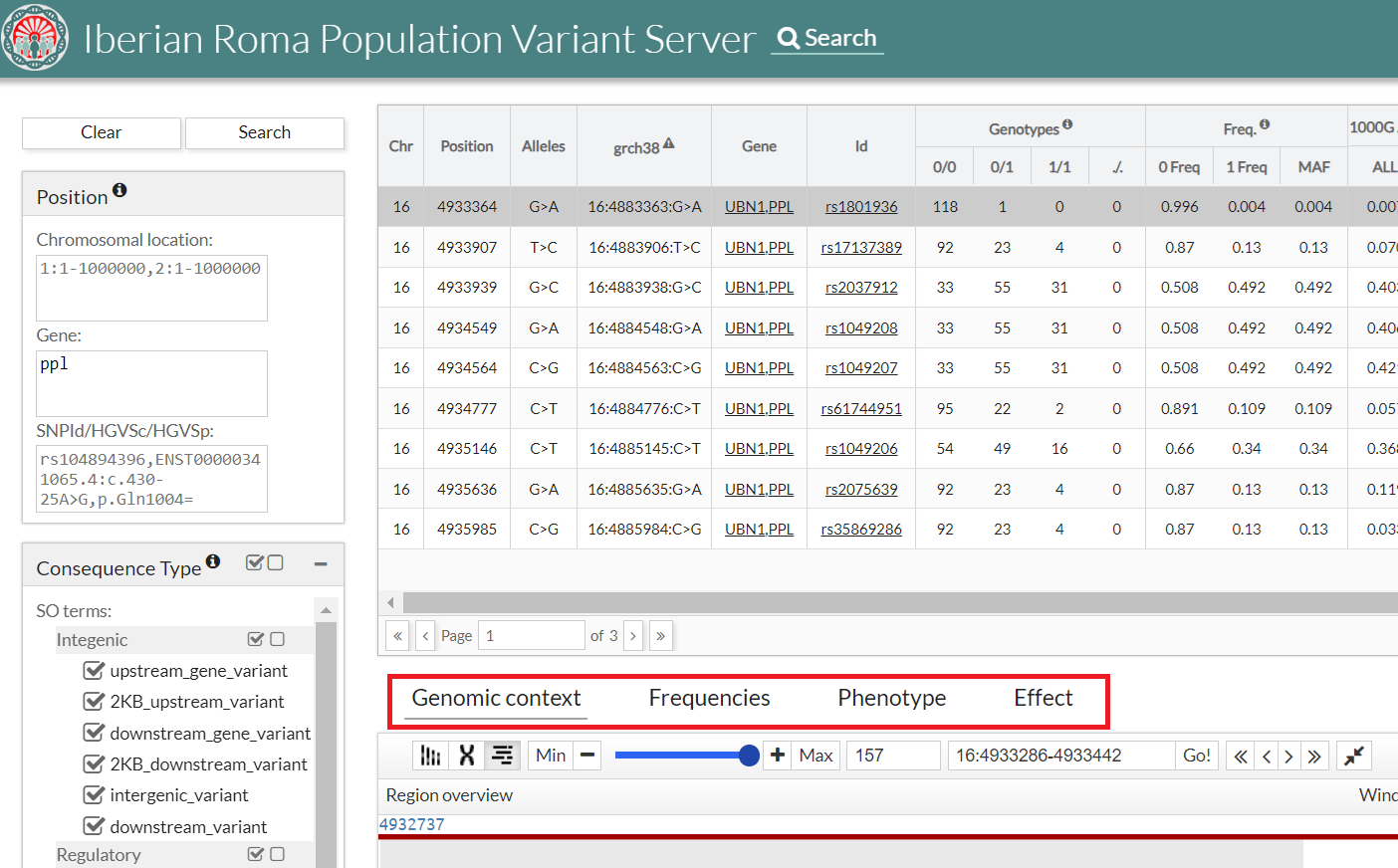

Genomic context
In this tab, the variant
within the genome is contextualized. If zoom in, the nucleotide
sequence of the reference genome GRCh37 is shown. The next tracks show genes and transcripts, SNP identifiers and variants of {{acronym}}. To move through the genome just click
and drag to the direction you want.
Zoom can be controlled through the corresponding buttons and karyotipe/chromosome panels can be selected
You can see more information, simply pointing the cursor over the region, gen, snp o variant.
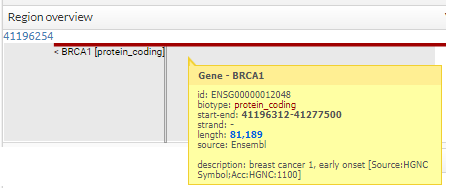
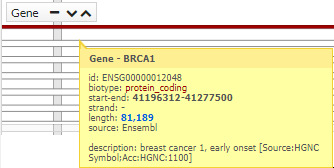
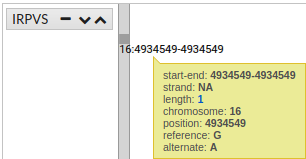
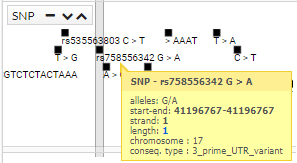
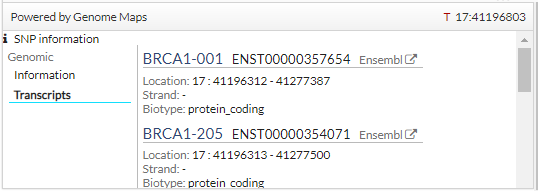
In addition, if clicking on a SNP, you get more information (transcripts):
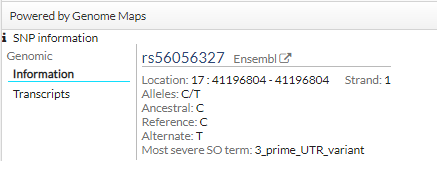
Zoom can be controlled through the corresponding buttons and karyotipe/chromosome panels can be selected

You can see more information, simply pointing the cursor over the region, gen, snp o variant.




In addition, if clicking on a SNP, you get more information (transcripts):


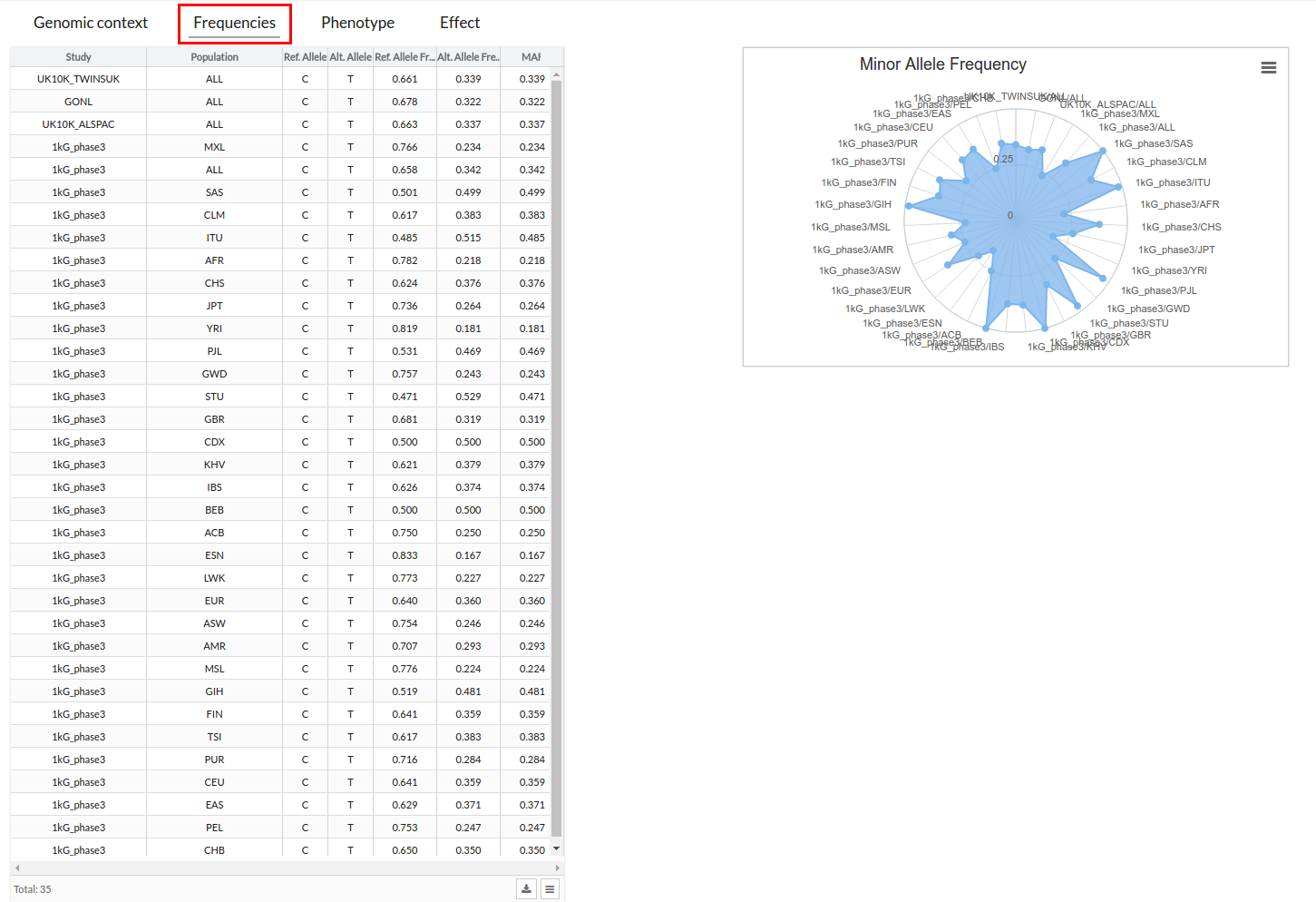
Frequencies
In this section you can see the different frequencies in the form of a table and a graph.

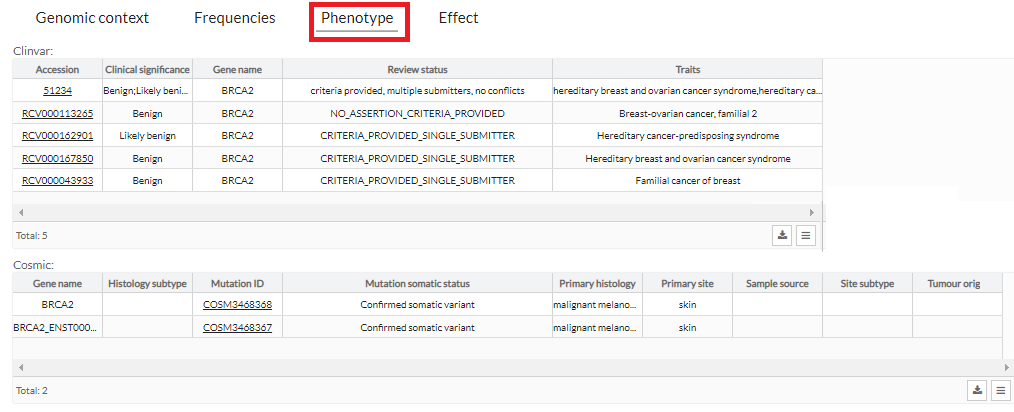
Phenotype
In the phenotypes tab we can see a more
extended
description of the phenotypes that the variant has in different databases.

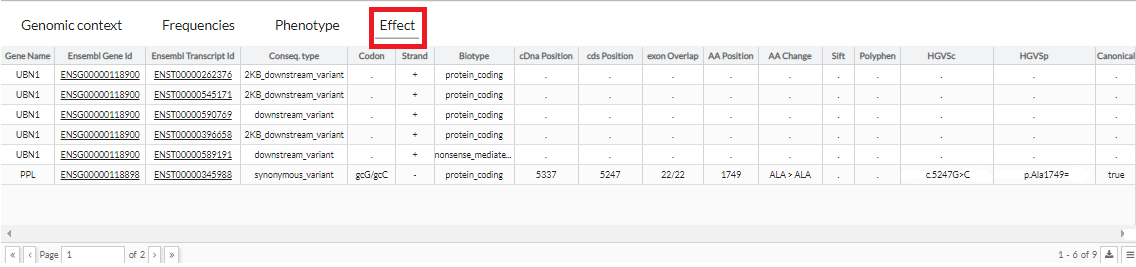
Effect
This tab shows the effect associated with the region where the variant is located in
Ensembl database.

Information and contact
In the upper right part of the page, if clicking on ? button, different options will appear:


- Documentation: Clicking shows the homepage of this documentation.
- Source code: Clicking takes you to the {{acronym}} source code hosted on github.
- Send an email:The user can send an email to info@clinbioinfosspa.es or you can use the
maintenance service of the {{acronym}} tool. In the subject you can select the reason for your
email:
- Suggest: suggestions on changes to the tool.
- Question: for other things such as if you are interested in contacting the user who has contributed the variant to the {{acronym}}.
- Error: to report a bug of the tool.
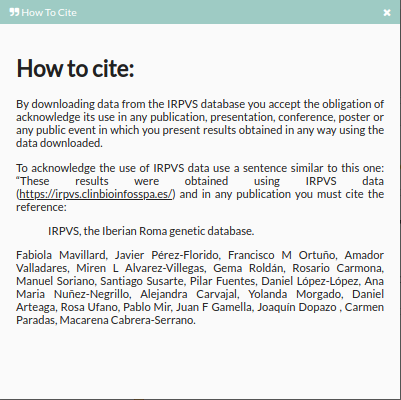
- How to cite: Clicking shows conditions to use {{acronym}} database.
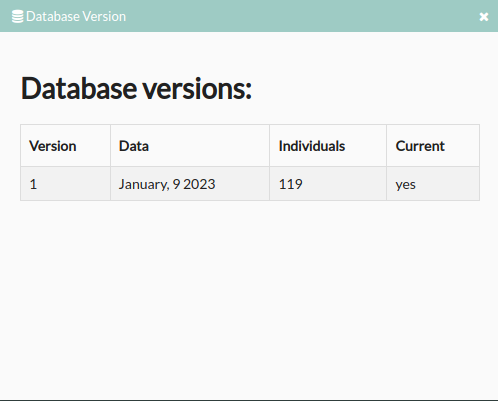
- Database versions: Clicking shows the info about database versions.